Contents
Monitoring your blood pressure at home is an essential part of managing your health, especially if you have conditions like hypertension. Accurate measurements can help you and your healthcare provider make informed decisions about your treatment. However, many people are unsure how to properly measure their blood pressure, which can lead to inaccuracies and misinterpretations.
Understanding the proper techniques and tools for measuring blood pressure at home is crucial for maintaining your cardiovascular health. With the right information, anyone can learn to accurately monitor their blood pressure, identify potential health issues early, and contribute to a more proactive approach to health care.
In this article, we’ll explore practical steps to measure your blood pressure accurately at home, ensuring that you have a reliable way to track your health.
Measuring blood pressure isn’t just about using a machine; it involves understanding the factors that affect readings and knowing how to prepare for the measurement. This comprehensive guide will help you navigate through the process, understand the equipment, and interpret your readings, ensuring that you maintain accurate blood pressure records.
By following these tips, you’ll not only gain confidence in self-measuring but also play an active role in your health management.
Why Measuring Blood Pressure Matters
Understanding your blood pressure is vital for several reasons. Regular monitoring helps in early detection of potential health issues, allowing for timely interventions. Here are a few key points to consider:
Understanding Hypertension – A Silent Killer
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is often referred to as a silent killer because it may not present any obvious symptoms. Regular monitoring can help you catch this potentially dangerous condition before it leads to serious health problems such as heart disease or stroke.
Being proactive and keeping track of your blood pressure can significantly reduce the risks associated with hypertension. Knowing your numbers allows you to make lifestyle changes or follow medical advice more effectively.
Tracking Your Progress – A Tool for Better Health
Recording your blood pressure readings over time provides valuable insights into your cardiovascular health. This data can help you and your healthcare provider assess the effectiveness of any treatment plans or lifestyle changes.
Documenting your readings can help identify patterns or triggers that may influence your blood pressure. Keeping a log will also facilitate discussions with your healthcare provider, leading to more tailored and effective interventions.
Choosing the Right Equipment
Before you can accurately measure your blood pressure, you need the right tools. The most common devices used at home are automatic digital monitors, but there are several options available.
Types of Blood Pressure Monitors
There are primarily three types of blood pressure monitors: digital, manual, and wrist monitors. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages:
- Digital Monitors: These are user-friendly and provide quick results. Ideal for most people, they come with features like memory storage and averaging of readings.
- Manual Monitors: These require a stethoscope and are usually used in clinical settings. They can be less practical for home use but may provide more accurate readings when used correctly.
- Wrist Monitors: While convenient, wrist monitors can be less reliable if not positioned correctly. They are best used by individuals who cannot use upper arm monitors.
Calibration and Maintenance
To ensure accuracy, regularly calibrate your blood pressure monitor according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Check the device with your healthcare provider at least once a year. Additionally, keep the monitor clean and store it in a safe place to avoid damage.
Preparing for the Measurement
Preparation is crucial for obtaining accurate blood pressure readings. Several factors can influence your blood pressure, so following specific steps is essential.
Timing Your Measurement
Blood pressure can fluctuate throughout the day based on various factors like stress, diet, or physical activity. Measure your blood pressure at the same time every day for consistency—preferably in the morning before any medications or meals.
Allowing a few minutes of relaxation before measuring can also help ensure that your readings are accurate. Avoid measuring during stressful situations or after consuming caffeine or nicotine.
Proper Positioning
Your body position during measurement plays a significant role in accuracy. Sit in a comfortable chair with your back supported, feet flat on the ground, and legs uncrossed. Rest your arm at heart level on a flat surface, such as a table, to avoid influence from gravity.
Ensure that the blood pressure cuff fits properly—too loose or too tight can yield inaccurate results. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for cuff placement, usually around 1 inch above the elbow.
Taking the Measurement
Now that you’re prepared, it’s time to take your blood pressure measurement. Following the correct procedure will help ensure accurate results.
Step-by-Step Guide to Measuring Blood Pressure
- Attach the Cuff: Wrap the cuff around your upper arm and secure it snugly, following the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Start the Monitor: Press the start button on digital monitors and allow the device to inflate automatically. For manual monitors, inflate the cuff using the bulb until the gauge reads around 30 mmHg above your expected systolic pressure.
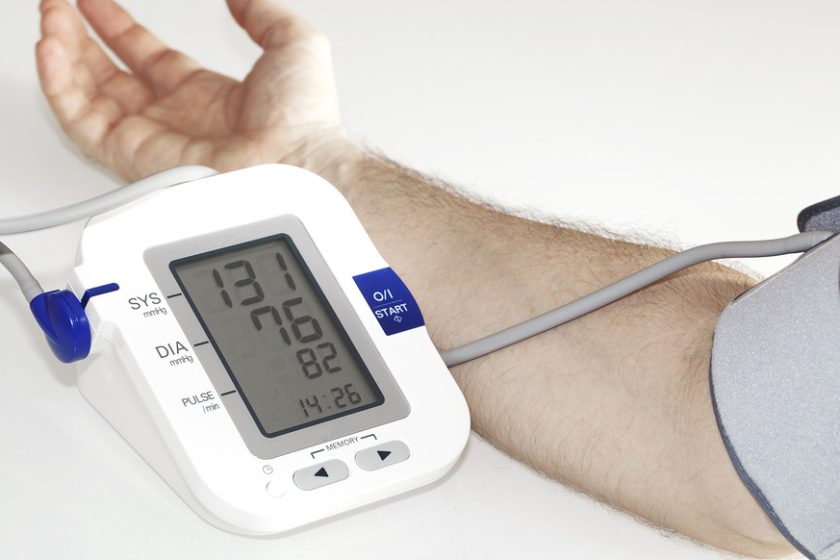
- Read the Results: Once the cuff deflates, note the systolic (top number) and diastolic (bottom number) pressures displayed. A healthy reading is typically around 120/80 mmHg.
- Repeat for Accuracy: Take two or three readings, one minute apart, and average the results for greater accuracy.
Understanding Readings
Interpreting your blood pressure readings is straightforward but crucial. A reading below 120/80 mmHg is considered normal, while 120-129/less than 80 mmHg is elevated blood pressure. Hypertension is categorized as 130/80 mmHg or higher.
Consult your healthcare provider if you consistently measure elevated readings. Keeping a log of your results can help in managing your health more effectively.
Measuring your blood pressure at home is an effective way to stay on top of your health. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can ensure that your measurements are accurate and meaningful. Regular monitoring helps you understand your body better and take proactive steps to maintain your well-being. Always consult with a healthcare professional if you have concerns about your readings or overall health. Remember, managing your blood pressure effectively starts with knowledge and routine practice.